The human ankle is a complex joint that facilitates a wide range of movements, including foot inversion. Foot inversion is the movement of the foot inward, where the sole of the foot is turned towards the midline of the body. This movement is crucial for balance, stability, and overall mobility. In this article, we will delve into the world of foot inversion, exploring its anatomy, biomechanics, and significance in various activities.
Key Points
- The ankle joint is a complex structure composed of bones, ligaments, and muscles that work together to facilitate foot inversion.
- Foot inversion is essential for balance, stability, and mobility, and is used in various daily activities and sports.
- The peroneal muscles, particularly the peroneus longus and peroneus brevis, play a crucial role in controlling foot inversion.
- Weak or imbalanced peroneal muscles can lead to ankle instability and increased risk of injury.
- Strengthening the peroneal muscles through exercises such as ankle circles and heel raises can help improve ankle stability and reduce the risk of injury.
Anatomy of Foot Inversion

The ankle joint is a synovial hinge joint that connects the distal ends of the tibia and fibula bones in the leg to the talus bone in the foot. The joint is surrounded by a complex network of ligaments, tendons, and muscles that work together to facilitate movement. The muscles responsible for foot inversion are the peroneal muscles, which include the peroneus longus and peroneus brevis. These muscles are located on the lateral aspect of the leg and attach to the foot via tendons.
Biomechanics of Foot Inversion
Foot inversion occurs when the peroneal muscles contract, pulling the foot inward. This movement is facilitated by the shape of the ankle joint and the arrangement of the ligaments and tendons. The talus bone, which forms the upper part of the ankle joint, is shaped in such a way that it allows for a wide range of movement. The ligaments and tendons surrounding the joint provide stability and support, allowing the peroneal muscles to control the movement of the foot.
The movement of foot inversion can be divided into three stages: initial contact, mid-stance, and push-off. During initial contact, the foot strikes the ground and the peroneal muscles contract to stabilize the ankle. In mid-stance, the peroneal muscles continue to contract, controlling the movement of the foot as it rolls inward. Finally, during push-off, the peroneal muscles relax, allowing the foot to return to its neutral position.
| Muscle | Function |
|---|---|
| Peroneus Longus | Controls foot inversion and eversion |
| Peroneus Brevis | Assists in foot inversion and stabilizes the ankle |
| Tibialis Anterior | Supports the arch of the foot and assists in foot inversion |
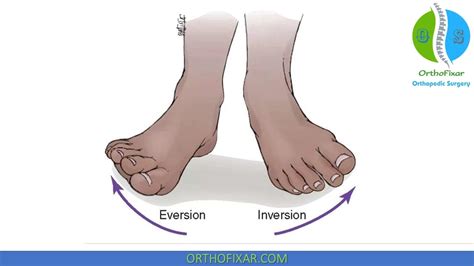
Significance of Foot Inversion

Foot inversion is essential for balance, stability, and mobility. It is used in various daily activities, such as walking, running, and climbing stairs. In sports, foot inversion is critical for activities such as tennis, basketball, and soccer, where quick changes of direction are required. The ability to control foot inversion is also important for maintaining balance and preventing falls.
Training and Exercise
Training and exercise can help improve foot inversion and overall ankle stability. Exercises such as ankle circles, heel raises, and single-leg balances can help strengthen the peroneal muscles and improve proprioception (awareness of body position and movement). It’s essential to start with low-intensity exercises and gradually increase the difficulty as the muscles strengthen.
In addition to exercises, proper footwear and orthotics can also help support the ankle and improve foot inversion. Shoes with good arch support and a stable sole can help reduce the risk of injury and improve overall ankle stability.
What is the primary function of the peroneal muscles?
+The primary function of the peroneal muscles is to control foot inversion and eversion, as well as stabilize the ankle joint.
How can I improve my foot inversion?
+You can improve your foot inversion by strengthening the peroneal muscles through exercises such as ankle circles and heel raises. Proper footwear and orthotics can also help support the ankle and improve foot inversion.
What are the consequences of weak or imbalanced peroneal muscles?
+Weak or imbalanced peroneal muscles can lead to ankle instability and increased risk of injury. This can result in chronic ankle pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
In conclusion, foot inversion is a complex movement that requires the coordinated effort of multiple muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Understanding the anatomy and biomechanics of foot inversion can help improve overall ankle stability and reduce the risk of injury. By incorporating exercises and proper footwear into your daily routine, you can improve your foot inversion and maintain optimal ankle health.
