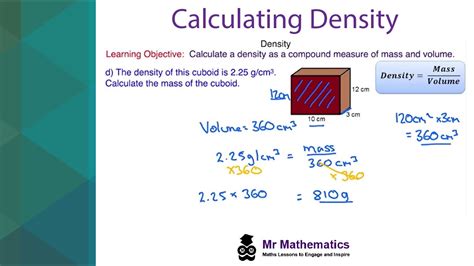
Calculating density is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, and it's essential to understand the process to work with various materials and substances. Density is defined as the mass per unit volume of a substance, and it's typically expressed in units such as kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) or grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³). In this article, we'll delve into the world of density calculation, exploring the concepts, formulas, and applications of this crucial physical property.
Key Points
- The formula for calculating density is ρ = m/V, where ρ is the density, m is the mass, and V is the volume.
- Density is a scalar quantity, and its unit is typically expressed in kg/m³ or g/cm³.
- Relative density, or specific gravity, is the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of water at a reference temperature.
- Density calculation has numerous applications in physics, engineering, chemistry, and biology.
- Understanding density is crucial for designing and optimizing systems, materials, and processes in various industries.
Understanding the Concept of Density

Density is a measure of how much mass is packed into a given volume of a substance. It’s an intrinsic property of the material, meaning it doesn’t depend on the amount of substance present. The concept of density is closely related to the concept of mass and volume. Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, while volume is a measure of the amount of space occupied by the object. By dividing the mass by the volume, we get the density of the substance.
Formula for Calculating Density
The formula for calculating density is straightforward: ρ = m/V, where ρ (rho) is the density, m is the mass, and V is the volume. This formula shows that density is directly proportional to mass and inversely proportional to volume. In other words, if you increase the mass of an object while keeping its volume constant, its density will increase. Conversely, if you decrease the volume of an object while keeping its mass constant, its density will also increase.
| Property | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mass (m) | Kilograms (kg) | Amount of matter in an object |
| Volume (V) | Cubic meters (m³) | Amount of space occupied by an object |
| Density (ρ) | Kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) | Mass per unit volume of a substance |

Relative Density and Specific Gravity

Relative density, also known as specific gravity, is the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of water at a reference temperature. This property is useful for comparing the densities of different substances. Specific gravity is defined as the ratio of the density of the substance to the density of water at 4°C (39.2°F), which is approximately 1000 kg/m³. For example, the specific gravity of gold is around 19.3, meaning it’s 19.3 times denser than water.
Applications of Density Calculation
Density calculation has numerous applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, chemistry, and biology. In physics, density is used to calculate the weight of an object, the buoyancy force, and the pressure exerted by a fluid. In engineering, density is used to design and optimize systems, such as bridges, buildings, and pipelines. In chemistry, density is used to identify substances, calculate concentrations, and predict the behavior of mixtures. In biology, density is used to study the properties of biomolecules, cells, and tissues.
What is the difference between density and specific gravity?
+Density is the mass per unit volume of a substance, while specific gravity is the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of water at a reference temperature.
How do you calculate the density of a mixture?
+The density of a mixture can be calculated using the formula: ρ = (m₁ + m₂ +... + mₙ) / (V₁ + V₂ +... + Vₙ), where ρ is the density of the mixture, mᵢ is the mass of each component, and Vᵢ is the volume of each component.
What are some common units of density?
+Some common units of density include kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³), grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³), and pounds per cubic foot (lb/ft³).
In conclusion, calculating density is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, and it’s essential to understand the process to work with various materials and substances. By mastering the formula for calculating density and understanding the concepts of relative density and specific gravity, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle a wide range of problems in various fields. Whether you’re designing a new material, optimizing a system, or studying the properties of biomolecules, density calculation is a crucial tool in your toolkit.